As a dog owner, it’s common to notice your dog skin problems. However, when a dog experiences excessive itching, scratching, or chewing at their skin, it may indicate a more serious issue—specifically, dog skin problems. Observing your dog’s skin can provide valuable insights into their overall health, as it often reflects their internal condition. All Dogs regardless of breed or age, can be susceptible to skin issues. However, young dogs, older dogs, and those living in unhealthy environments may be at a greater risk.
Common Skin Problems in Dogs
There are several skin conditions that your dog may encounter, each with its own causes and treatment options. Here are some of the most common skin problems in dogs:
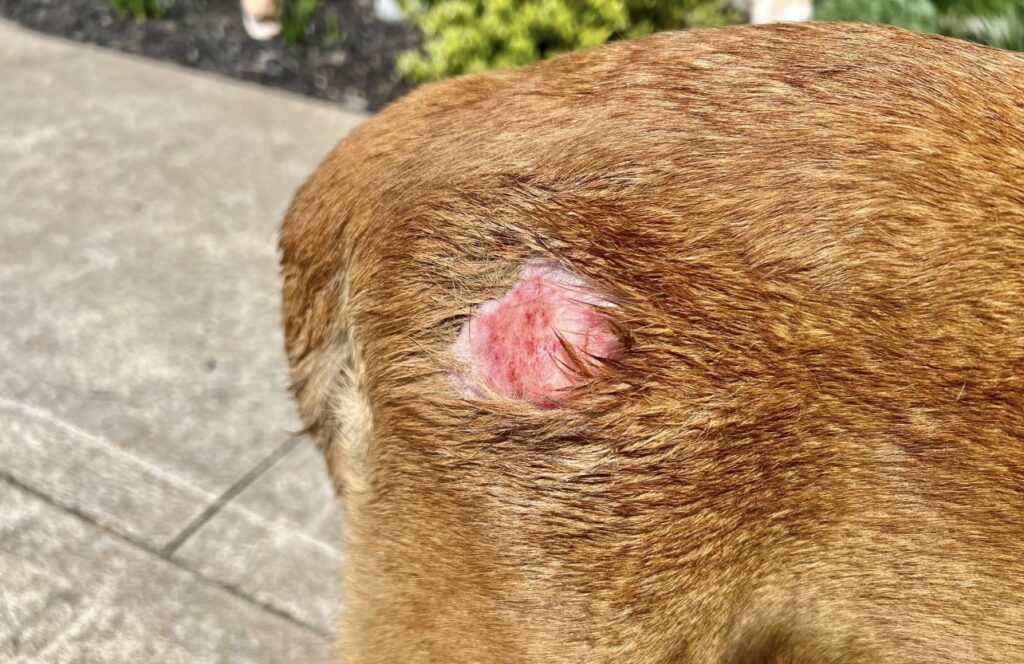
1. Hot Spots: Also known as acute moist dermatitis, hot spots are inflamed, painful patches that can develop rapidly. They often arise from excessive licking or scratching and can lead to infection.
2. Dry Skin: Many dogs suffer from dry, flaky skin, which can lead to itching and irritation. Environmental factors, like low humidity, or allergens can contribute to this condition.
3. Acral Lick Granuloma: This occurs when a dog repetitively licks a specific area, causing thickened, inflamed skin. It can be challenging to treat and often requires both topical treatments and behavioral modifications.
4. Yeast Infections: Yeast infections often occur in warm, moist areas of your dog’s body, such as their ears or between their toes. Dogs with compromised immune systems may be more prone to such infections, leading to severe itching and discomfort.
5. Allergic Dermatitis: Dogs can develop allergies to various substances, including pollen, dust mites, or certain food ingredients. Symptoms generally manifest as itching, redness, and inflammation.
6. Impetigo: This bacterial skin condition typically affects young dogs and appears as pustules or sores around the belly and groin area.
7. Hair Loss: While seasonal shedding is normal, significant hair loss can indicate underlying skin conditions or hormonal imbalances. It can be distressing for both the dog and the owner.
8. Color or Texture Changes: Changes in skin color, consistency, or thickness can signal various skin conditions or immune system attacks.
Understanding these common skin problems is vital for all dog owners, as early detection can lead to more effective treatment.
Diagnosing Skin Issues
When you take your dog to the vet, they will usually perform a thorough examination to determine the underlying cause of your dog’s skin problems. Diagnosis may involve several methods:
1. Skin Biopsy: A sample of the affected skin may be taken for laboratory analysis to identify specific skin conditions or infections.
2. Microscopic Examination: Your vet may examine skin and hair samples under a microscope to check for parasites like fleas or mites.
3. Allergy Testing: If allergies are suspected, your veterinarian may recommend blood tests or skin tests to pinpoint specific allergens.
4. Fungal Cultures: To confirm fungal infections like ringworm, your vet may perform cultures to identify the causative organism.
5. Blood Tests: Comprehensive blood tests can help assess your dog’s overall health and identify any hormonal imbalances or immune system attacks.
Once a diagnosis has been made, your veterinarian can recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Treating Dog Skin Problems
Treatment options for dog skin problems can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options your vet may suggest:
1. Medicated Shampoos: Special shampoos can help treat skin infections, remove allergens, and soothe irritated skin. It is essential to use products specifically formulated for dogs to ensure safety and effectiveness.
2. Topical Ointments: Your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics or corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation and control infections. These ointments can be applied directly to the affected areas for targeted relief.
3. Oral Medications: Depending on the diagnosis, your veterinarian might prescribe oral medications such as antibiotics, antihistamines, or corticosteroids to alleviate symptoms and combat infections. These medications can help reduce itching and inflammation.
4. Dietary Adjustments: If food allergies are suspected, your vet may recommend a hypoallergenic diet to eliminate potential triggers. This can help improve your dog’s skin condition from the inside out and ensure they receive the necessary nutrients.
5. Dietary Supplements: Supplements, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can promote skin health and reduce inflammation. These may be beneficial for dogs with chronic skin issues or those prone to dry skin.
6. Allergy Shots: For dogs with severe allergies, your veterinarian may recommend immunotherapy (allergy shots) to help desensitize your dog to specific allergens over time. This treatment can provide long-term relief from allergic reactions.
7. Behavioral Modification: If your dog’s skin condition is exacerbated by excessive licking or scratching, behavioral modification techniques may be necessary. This could include training, using cones or collars to prevent licking, or providing more physical activities to keep your dog occupied and distracted.
Preventing Skin Issues
Preventing skin problems in dogs is often easier than treating them once they arise. Here are some proactive steps you can take to minimize the risk of dog skin problems:
1. Regular Grooming: Frequent brushing helps remove dirt, debris, and loose fur, which can reduce the risk of skin irritation. Regular grooming sessions also allow you to check your dog’s skin for any abnormalities or changes.
2. Use Hypoallergenic Products: Opt for grooming products specifically designed for dogs, particularly hypoallergenic ones, to minimize the risk of skin irritation.
3. Provide a Healthy Diet: Ensure your dog is eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients. Consult your veterinarian for recommendations on high-quality dog food and supplements that support skin health.
4. Maintain Environmental Hygiene: Keeping your home clean by regularly vacuuming and washing your dog’s bedding can help reduce exposure to allergens like dust mites, pollen, and other irritants that can contribute to skin problems.
5. Manage Stress: Dogs can experience stress, which may lead to skin issues or exacerbate existing conditions. Create a calm, stable environment for your dog, and engage in regular exercise, training, and playtime to keep them mentally and physically stimulated.
6. Monitor for Allergens: Be observant of your dog’s reactions to certain environmental factors. If you notice increased itching during specific seasons, it may be due to pollen or other allergens. Consult your veterinarian for potential allergy testing and management options.
7. Keep Up with Veterinary Checkups: Regular veterinary visits can help catch any skin problems early. Your vet can provide vaccinations, parasite control, and general health checkups that contribute to your dog’s overall well-being.
Dog skin problems can significantly affect your pet’s quality of life if not addressed promptly. By being vigilant and understanding the common skin conditions that dogs can experience, you can take proactive steps to protect your pet from unnecessary discomfort.











